Osteochondria is the most severe form of degenerative -twinkling spine damage, which is based on the defeat of the multipurpose core and the management of the neuroderarous disc, with the subsequent deformities of the adjacent vertebrae bodies, the interdisciplinary joints.
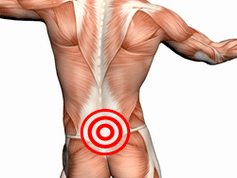
One of the most common forms of osteochondrication is the lumbar osteochondria or, more specifically, the lumbar spine.For many - both men and women - they are familiar with back pain in the lower back, sanctuary, lower extremities, caused by various types of lumbar osteochondicity and its complications.Among the reasons for temporary disability and disability, this disease occupies one of the first parts.
The course of the disease is chronic, usually with periods of frenzy.Most of the time, the exacerbations of lumbar lift osteochondroxis and the transfer of weights, hypothermia, stress and injury.
Lumbar spine osteocondrium - causes mechanism
There was no clear cause of osteochondicism, the disease is considered to be multiplied.The most popular theory is, according to which the cause of the spine osteochondryosis is the constant overwhelming position of the muscles or muscle hypotension, the abnormal muscle tension, which leads to the overload of the vertebral parts, the deterioration of the benefit of the blood supply, whichThe result is the result that is the result that is the result which is the result that is the result is the result of the result that is the result of being the result of being the result of being the result of the intertebral.Osteochondria.
The cause of premature aging of intervertebral discs can also be endocrine and metabolic disorders, a hereditary predisposition to the development of osteochondination, autoimmune disorders and microva.The negative role of the visceral, that is, related to the internal organs, the pathologies in the development of spine osteochondral has also been proven.An important role in the development of the disease belongs to unwanted heredity.The contribution of the inheritance factors to the appearance of lumbar osteochondrication is about 60%, the remainder refers to the factors of the unfavorable external effect on the spine.
Factors that contribute to the development of osteochondicity in both lumbar and other parts of the spine are very numerous.The main of these: inappropriate posture, subdivision, muscle hypertension in the lumbar region as a result of steady weight wear or a strong excessive load, hormonal restructuring, endocrine and physical illnesses, violation of normal blood supply, blood supply to the tissue.Under the influence of these factors on spine structures, the processes of dehydration and circulatory disorders, articulation and underground joints, developing bones and discs - the hernias are gradually increasing.
The most obvious causes of lumbar osteochondryosis are considered to be a more frequent sedentary lifestyle and injury to the back.As a result, the risk group mainly includes those people whose profession is directly related to loads on the back.This is a very wide range of professions - seller and waiters, surgeons and teachers - all who are forced to spend most of the working time.The risk group includes manufacturers and travel, as well as athletes who, in the nature of the activity, have large loads in the spine.In addition, the drivers, the various office officials, the developers - that is, those who have the project mainly seating and suffering from hypotherapy, suffer from lumbar osteochondria.
Lumbar spine osteochondal symptoms
TolumbarThe painful sensations of different nature are possible.This can be either a cunning pain that occurs with a prolonged seat or after sleeping, as well as sharp shooting, causing the most unpleasant posture and does not allow the opportunity to align.The pain is pinched by nerve roots, irritation of their own spine nerves, edema and irritation of the muscles and joints found in the zone integrated of the lumbar spine.
Pain syndrome can be caused by the compression of radical structures (rootopathy), spinal cord compression (compression of myelopathy), spinal cord damage due to reduced blood supply due to push, stenosis (stenosis).
The reason for the compression may be: the protrusion and the hernia of the intervertebral discs, the sponelum (sliding the vertebra forward relative to the subject), the development of osteophytes and cartilage tissue in the vertebral part.As a resultOsteochondria of lumbar regionThe spine leads to a stenosis of the channel through which the branch -scale nerves or vascular structures pass and under certain conditions (embarrassing movement, physical activity, unsuccessful body turning, etc.), compression (compression).Compression of nerve structures leads to various pain syndromes, muscle spasms.Compression of blood vessels causes a violation of blood supply - the ischemia of the organ supplying from this boat or artery begins.
Clinical osteochondryosis of the lumbar spine
The clinical picture for lumbar osteochondria is determined by a cluster of spine symptoms (change of static and dynamic lumbar spine) and accompanied symptoms, which are understood as a violation of the function of neurological and vascular structures in the spine.
Lumbar osteochondal vertebral syndrome
With lumbar osteochondria, the vertebral syndrome is characterized by the following complex of symptoms:
- Violation of the configuration of the functional-anatomical part of the spine: there is a leveling or (less frequent) increase in lordosis, scoliosis or lintosolification.
- Violation of mobility in the lumbar region, reduced volume of movement, muscle-oon imbalance caused by the intensity of both deep and surface multi-human muscle.
- Local pain and pain with active and passive movements, which cause intensity of the reflex tonic muscles.
- Violation of spring-mobile functions of both the intervertebral disc and, in general, the vertebrate kinetic section.
- Local pain (increased sensitivity) of the bone-binding structures of the spine in the affected area (pain during palpation, local (regional) spine and/or pain syndrome).
It is important to note that with the lumbar spine, there are always pathologies of vertebral pathologies.The presence of signs of myelopathy, rhizopathy and myeradicism without obvious clinical and morphological signs of spine syndrome, as a rule, as a rule, as a rule, a deeper examination of the patient for the main damage to the nervous system.
Extrovertebral (Reflex and Compression) syndromes for osteochondria of lumbar spine
Extroverted syndromes are divided into two large groups: reflex and compression.
Reflex syndromesThey precede compression and are caused by the irritation of the nerve root receptors emerging from the vertebral canal through the intervertebral holes.Irritation can be caused by intervertebral hernia, bone developments, and vascular disorders (edema, blood circulation worsens) and inflammation.In some cases, this leads to intensive pain, which occurs not only locally, but also during the nerve at a distance from the place of irritation -the "reflected pains", the reflected pain can be short and acute ("displacement" or stupid.(burning, gooseberries, reduced sensitivity).
Reflection syndromes include Lumbago ("Shift") in the acute development of disease and Lumbalgia with underlying or chronic course.
Compression syndromes are syndromes that occur as a result of compression, nerve violations, blood vessels, spinal cord in the lumbar vertebral area.Compression syndromes for lumbar osteochondria are divided into radical and vascular-brown.A specific case of compression syndrome is myelopathy - violation of the spinal cord.
Treatment syndromes (radiopathy) are usually due to disc protrusions, causing a violation of cerebrospinal roots.The radical symptoms resulting in this case correspond to the level of the affected spine.Most of the time, the roots of the L4-S1 are affected.
Vascular-brown neurological disorders are caused by the compression of the hernia in the spine and the root passing with it.At the same time, the "paralytic isshias" can be devastatingly developed, characterized by regional decline or paralysis of the muscle of the legs of the legs.In such cases, the occurrence of motor disorders is accompanied by the disappearance of pain.
Even more serious neurological manifestations are caused by a violation of blood supply to the spinal cord due to damage to the radical arteries.At the same time, chronic myelopathy of the discipline, usually at the level of lumbar spinal cord thickening.
The most unfavorable version of lumbar vertical radical syndromes is the compression of the "horse tail" - the SO - called the tail syndrome.Most of the time, it is caused by the downward hernia of the disk, which compresses all the roots at the level of the affected part.
What is lumbar spine osteochondria?What are its symptoms?How to cure lumbar osteochondria?
Clinical classification of lumbar osteochondicity.Degree
Sorting lumbar osteochondicism according to diplomas is used for the systematic characteristics of clinical manifestations of the disease.This classification systematically describes the symptoms of the disease and begins as the patient has pain.
1 degree of osteochondic
It occurs when the intervertebral disc caused by a sharp movement or exaggeration.It is manifested by a sudden pain, in the spine a feeling of electricity transition arises, the muscles are inhibitory strained.
2 degree of osteochondal
The second degree can be manifested in the form of symptoms of the intervertebral protrusion and spine instability.Chronic pain that increases in loads.The intervals of recession and exacerbations alternate.The cervical area is characterized by throat pain, increasing after a long stay in a position, headaches, hand pain, shoulder pain, periodic discomfort or numbness on the fingers.For lumbar region - back pain, gluten pain, periodic pain in the sanctuary, frequent fatigue in the legs.
3 degree of osteochondal
It manifests in the form of symptoms of the intervertebral disc hernia (pain along the affected nerve, numbness of the hands or legs, a change in gait, headaches) or remote symptoms of the sacred hernia.Violation of heart rate, difficulty breathing.
4 degree osteochondal
It is generally accepted that the fourth degree of osteochondrialism begins when the hernia no longer manifests, manifestations of the disease can be reduced, but the symptoms of spine instability, slip or turn of the vertebrae or complete stabilization are still related.The manifestations of spinal cord developments (osteophytics) can be integrated into them, which can also squeeze spinal nerves or overlap the vertebral canal (secondary stenosis of the spine) and compress the spinal cord.In addition, the fourth grade involves the consequences of surgery if the hernia was removed immediately (various types of injection, consonance, inflammation).
Treatment of the lumbar spine of the spine
With the first acute lower back pain, it is necessary to consult a doctor to make a diagnosis to rule out a kidney colic, appendicitis or any other disease that requires medical emergency care.
If the cause of back pain is also known and this deterioration of the lumbar spine osteochondicity, first of all, it is necessary to maximize the load on the spine.It is necessary to observe the bed for 3 to 7 days - sometimes only this can significantly reduce pain.But in order to accelerate recovery, it is necessary, that is, effective, treatment.It should stimulate its own protective and health processes in the human body.Treatment should take into account the detection of the damage, the stage of the disease, the functional condition of the body and its individual systems.Surgical treatment of this disease is indicated only in very severe cases.Most of the time, various methods of conservative treatment of osteochondry are used.
Conservative treatment of lumbar osteochondicity
Conservative treatment methods are, first of all, drug therapy.In order to reduce the pain, as well as the decrease in inflammation, which is often the cause of the spine, non -chapite anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAID) in the form of tablets or - in acute cases - in the form of injections.Sometimes, after injection, an analgesic, the pain relaxes and does not repeat even when the duration of the drug ends.This means that it was possible to break the vicious cycle in which the pain leads to muscle cramps and the muscle tension, in turn, enhances the pain.However, if the pain lasts for a long time, it is important to remember that NSAIDs usually have various side effects and with prolonged use can cause unwanted complications - a decrease in the number of leukocytes in the bloodstream, complications from the gastrointestinal tract.
Often, sedative (soothing) factors are prescribed to improve the general condition of patients within 1-3 weeks, as well as small doses of antidepressants.With the lumbar spine bone, if necessary, novocaine is produced.Recently, anticopia drugs have begun to be used successfully to relieve pain.
To reduce compression syndromes, manual therapy, adhesion treatment (spine) and in special cases used - surgery.
When weakening the properties of stabilizing the connection device and the consistency of the spine, it is recommended to use fastening devices - corsets, collars, sauces, etc. and patients with spine osteochondria are extremely important in the future to enhance their own corset.
After removing acute symptoms, the task of creating muscle stabilization comes first in the first place and then stimulates the regeneration processes of damaged structures.To do this, use therapeutic gymnastics, reflexology, massage.To do this, use coarse protection (cartilage drugs).In addition to medicines that improve the condition of blood vessels (pottery protection), vitamins, mainly calcium group preparations that improve the condition of the tissue bone.
Widely used physiotherapeutic processes are used to treat the spine.They reduce tissue pain and edema, improve blood circulation and stimulate muscle stabilization.Procedures can be combined, alternating.Such methods of physiotherapeutic therapy as:
- Darsonvalization of the affected area of the rear and of the affected limbs.
- Electrophoresis?
- Low laser radiation.
- ultrasound;
- Exposure to the magnetic field.
- Thermal procedures.
The conditions of sanatorium, mud, ozkerite, paraffin, radon, sulphide, hydrogen, terentine and other baths are successfully used.
We must remember that for the development of full regeneration, it takes a fairly long period of time, under favorable conditions that occur in the sixth month.Therefore, the treatment should be great.It should be performed in a combined way, that is, combined medicines with physiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises.